Markets
Will the U.S. Get Hit With a Recession in 2024?
Subscribe to the Advisor Channel free mailing list for more like this
Will the U.S. Get Hit With a Recession in 2024?
This was originally posted on Advisor Channel. Sign up to the free mailing list to get beautiful visualizations on financial markets that help advisors and their clients.
For much of the last year, recession fears have been building against a sharp rise in interest rates and market uncertainty.
Only recently has there been a shift in sentiment. Given the resilience of the U.S. economy, a growing amount of investors are seeing an increasing likelihood of a soft landing—where the Federal Reserve raises interest rates to combat inflation without triggering a recession. However, many still remain cautious.
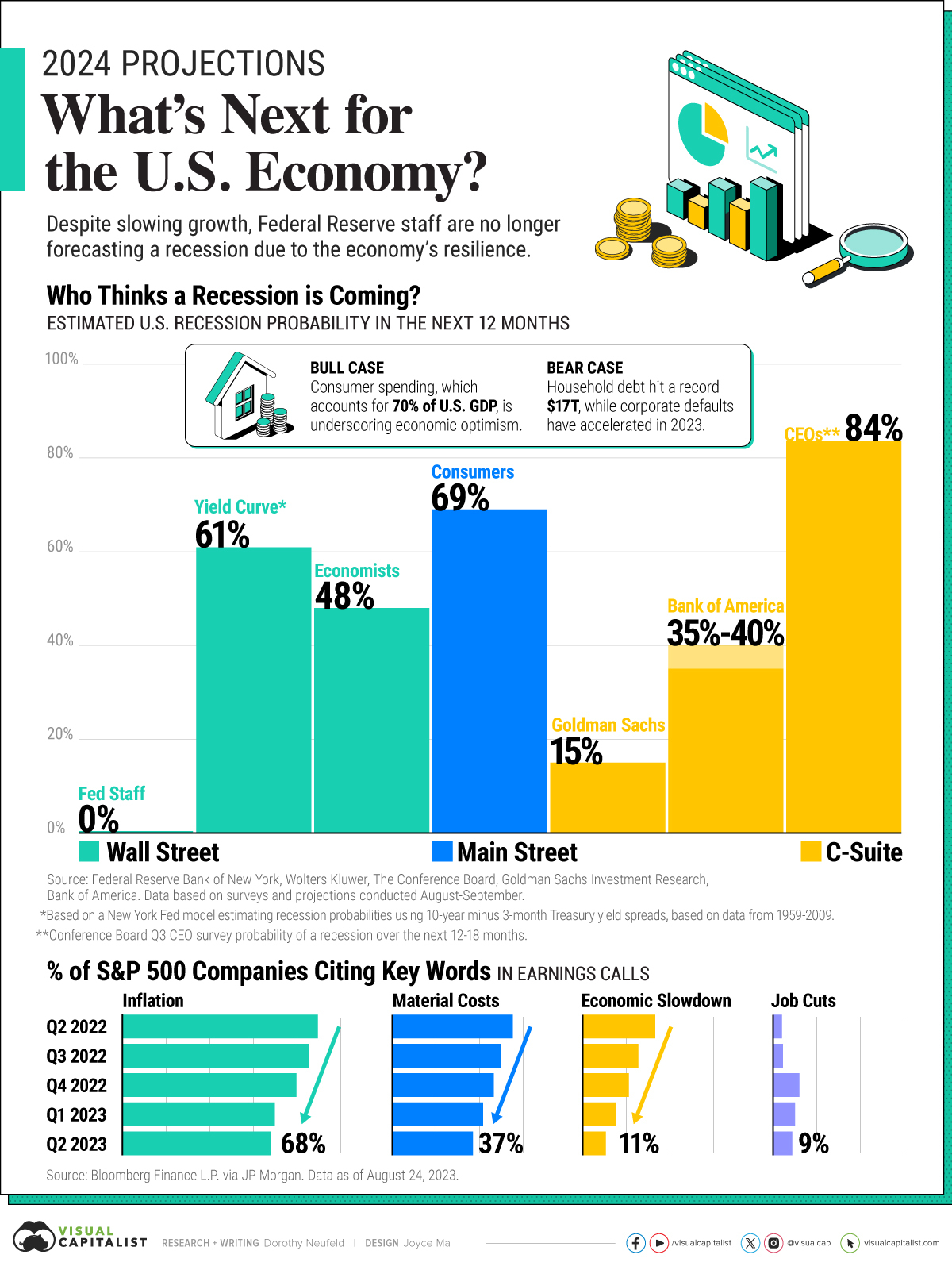
This graphic shows U.S. economic forecasts across Wall Street, Main Street, and C-Suite for 2024.
The Probability of a Recession in 2024
Here’s what key players are projecting for the economy:
| Forecaster | Estimated U.S. Recession Probability (Next 12 Months) |
|---|---|
| Federal Reserve Staff | 0% |
| Yield Curve* | 61% |
| Economists | 48% |
| Consumers | 69% |
| Goldman Sachs | 15% |
| Bank of America | 35-40% |
| CEOs** | 84% |
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of New York, Wolters Kluwer, The Conference Board, Goldman Sachs Investment Research, Bank of America. Data based on surveys and projections conducted August-September. *Based on a New York Fed model estimating recession probabilities using 10-year minus 3-month Treasury yield spreads, based on data from 1959-2009. **Conference Board Q3 CEO survey probability of a recession over the next 12-18 months.
In July, the Federal Reserve staff announced that they were no longer forecasting a recession in 2024, marking a sharp departure from earlier projections.
While the Fed staff continue to share a brighter outlook, the yield curve spread between 10-year and 3-month Treasury rates suggests there is a 61% change of a recession in the 12 months ahead. Historically, the yield curve has been a reliable predictor of recessions, based on a New York Fed model which uses data from 1959-2009.
Meanwhile, a survey of economists by Wolters Kluwer shows that they’re split, with 48% calling for a recession over the next 12 months.
Across Main Street, consumers share a more cautious sentiment, with over 69% saying that a recession is likely in the next year, based on a Conference Board survey.
Yet corners of America’s C-suite have grown more positive. Goldman Sachs recently dropped its recession forecast to a 15% likelihood while Bank of America gives it a 35-40% odds. On the other hand, 84% of CEOs are preparing for a recession in the next 12-18 months, a drop from 92% seen in the second quarter of 2023.
Bull Case vs. Bear Case Signals
Among the key factors investors are closely watching center around the impact of higher interest rates on the economy.
For the bull case, higher rates appear as though they haven’t significantly impacted consumer spending yet, although spending has slowed on non-essential items. Retail sales continue to be solid, and earnings across Home Depot, Walmart, Lowe’s, and other major retailers show resilience. Where the main changes are occurring are with consumers purchasing more affordable options.
However, consumers are relying increasingly on borrowing for spending.
For the bear case scenario, household debt has hit record highs of $17 trillion in March, rising 19% year-over-year. Higher rates have led these borrowing costs to jump, likely affecting household budgets. Meanwhile, corporate defaults have accelerated in 2023, and are projected to keep rising.
Overall, there are mixed signals across the wider economy, and it’s unclear if the country will experience or avoid a recession in 2024. Quantifying the full effects of higher interest rates on consumers and businesses remains an open question.
Mining
Ranked: The World’s Top Diamond Mining Countries, by Carats and Value
Who are the leaders in rough diamond production and how much is their diamond output worth?

Ranked: World Diamond Mining By Country, Carat, and Value
Only 22 countries in the world engage in rough diamond production—also known as uncut, raw or natural diamonds—mining for them from deposits within their territories.
This chart, by Sam Parker illustrates the leaders in rough diamond production by weight and value. It uses data from Kimberly Process (an international certification organization) along with estimates by Dr. Ashok Damarupurshad, a precious metals and diamond specialist in South Africa.
Rough Diamond Production, By Weight
Russia takes the top spot as the world’s largest rough diamond producer, mining close to 42 million carats in 2022, well ahead of its peers.
Russia’s large lead over second-place Botswana (24.8 million carats) and third-ranked Canada (16.2 million carats) indicates that the country’s diamond production is circumventing sanctions due to the difficulties in tracing a diamond’s origin.
Here’s a quick breakdown of rough diamond production in the world.
| Rank | Country | Rough Diamond Production (Carats) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇷🇺 Russia | 41,923,910 |
| 2 | 🇧🇼 Botswana | 24,752,967 |
| 3 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 16,249,218 |
| 4 | 🇨🇩 DRC | 9,908,998 |
| 5 | 🇿🇦 South Africa | 9,660,233 |
| 6 | 🇦🇴 Angola | 8,763,309 |
| 7 | 🇿🇼 Zimbabwe | 4,461,450 |
| 8 | 🇳🇦 Namibia | 2,054,227 |
| 9 | 🇱🇸 Lesotho | 727,737 |
| 10 | 🇸🇱 Sierra Leone | 688,970 |
| 11 | 🇹🇿 Tanzania | 375,533 |
| 12 | 🇧🇷 Brazil | 158,420 |
| 13 | 🇬🇳 Guinea | 128,771 |
| 14 | 🇨🇫 Central African Republic | 118,044 |
| 15 | 🇬🇾 Guyana | 83,382 |
| 16 | 🇬🇭 Ghana | 82,500 |
| 17 | 🇱🇷 Liberia | 52,165 |
| 18 | 🇨🇮 Cote D'Ivoire | 3,904 |
| 19 | 🇨🇬 Republic of Congo | 3,534 |
| 20 | 🇨🇲 Cameroon | 2,431 |
| 21 | 🇻🇪 Venezuela | 1,665 |
| 22 | 🇲🇱 Mali | 92 |
| Total | 120,201,460 |
Note: South Africa’s figures are estimated.
As with most other resources, (oil, gold, uranium), rough diamond production is distributed unequally. The top 10 rough diamond producing countries by weight account for 99.2% of all rough diamonds mined in 2022.
Diamond Mining, by Country
However, higher carat mined doesn’t necessarily mean better value for the diamond. Other factors like the cut, color, and clarity also influence a diamond’s value.
Here’s a quick breakdown of diamond production by value (USD) in 2022.
| Rank | Country | Rough Diamond Value (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇧🇼 Botswana | $4,975M |
| 2 | 🇷🇺 Russia | $3,553M |
| 3 | 🇦🇴 Angola | $1,965M |
| 4 | 🇨🇦 Canada | $1,877M |
| 5 | 🇿🇦 South Africa | $1,538M |
| 6 | 🇳🇦 Namibia | $1,234M |
| 7 | 🇿🇼 Zimbabwe | $424M |
| 8 | 🇱🇸 Lesotho | $314M |
| 9 | 🇸🇱 Sierra Leone | $143M |
| 10 | 🇹🇿 Tanzania | $110M |
| 11 | 🇨🇩 DRC | $65M |
| 12 | 🇧🇷 Brazil | $30M |
| 13 | 🇱🇷 Liberia | $18M |
| 14 | 🇨🇫 Central African Republic | $15M |
| 15 | 🇬🇾 Guyana | $14M |
| 16 | 🇬🇳 Guinea | $6M |
| 17 | 🇬🇭 Ghana | $3M |
| 18 | 🇨🇲 Cameroon | $0.25M |
| 19 | 🇨🇬 Republic of Congo | $0.20M |
| 20 | 🇨🇮 Cote D'Ivoire | $0.16M |
| 21 | 🇻🇪 Venezuela | $0.10M |
| 22 | 🇲🇱 Mali | $0.06M |
| Total | $16,290M |
Note: South Africa’s figures are estimated. Furthermore, numbers have been rounded and may not sum to the total.
Thus, even though Botswana only produced 59% of Russia’s diamond weight in 2022, it had a trade value of nearly $5 billion, approximately 1.5 times higher than Russia’s for the same year.
Another example is Angola, which is ranked 6th in diamond production, but 3rd in diamond value.
Both countries (as well as South Africa, Canada, and Namibia) produce gem-quality rough diamonds versus countries like Russia and the DRC whose diamonds are produced mainly for industrial use.
Which Regions Produce the Most Diamonds in 2022?
Unsurprisingly, Africa is the largest rough diamond producing region, accounting for 51% of output by weight, and 66% by value.
| Rank | Region | Share of Rough Diamond Production (%) | Share of Rough Diamond Value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Africa | 51.4% | 66.4% |
| 2 | Europe | 34.9% | 32.9% |
| 3 | North America | 13.5% | 52.8% |
| 4 | South America | 0.2% | 2.4% |
However diamond mining in Africa is a relatively recent phenomenon, fewer than 200 years old. Diamonds had been discovered—and prized—as far back as 2,000 years ago in India, later on spreading west to Egyptian pharaohs and the Roman Empire.
By the start of the 20th century, diamond production on a large scale took off: first in South Africa, and decades later in other African countries. In fact between 1889–1959, Africa produced 98% of the world’s diamonds.
And in the latter half of the 20th century, the term blood diamond evolved from diamonds mined in African conflict zones used to finance insurgency or crime.
-
 Money3 weeks ago
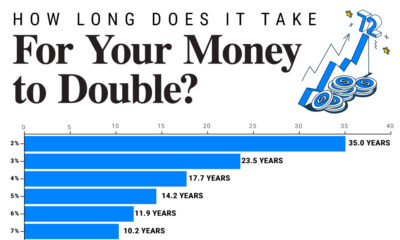
Money3 weeks agoVisualized: How Long Does it Take to Double Your Money?
-
 Markets1 week ago
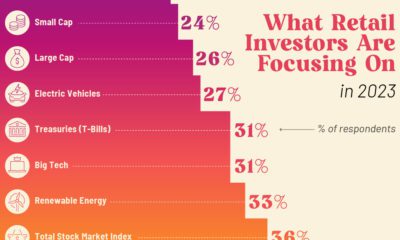
Markets1 week agoCharted: What are Retail Investors Interested in Buying in 2023?
-

 Maps3 weeks ago
Maps3 weeks agoThe Incredible Historical Map That Changed Cartography
-
 Markets6 days ago
Markets6 days agoThe $109 Trillion Global Stock Market in One Chart
-
 Markets4 weeks ago
Markets4 weeks agoCharted: Six Red Flags Pointing to China’s Economy Slowing Down
-

 VC+3 weeks ago
VC+3 weeks agoWhat’s New on VC+ in September
-
 Markets5 days ago
Markets5 days agoRanked: 15 of the World’s Least Affordable Housing Markets
-

 Markets4 weeks ago
Markets4 weeks agoThe 25 Best Stocks by Shareholder Wealth Creation (1926-2022)









 Creator Program
Creator Program